Ganglion Cyst are more common in women, and 70% occur in people between the ages of 20-40
Inputs by, Dr. Deepthi Nandan Reddy Adla , Senior Consultant Orthopedic Surgeon Continental Hospitals
What are Ganglion Cysts?
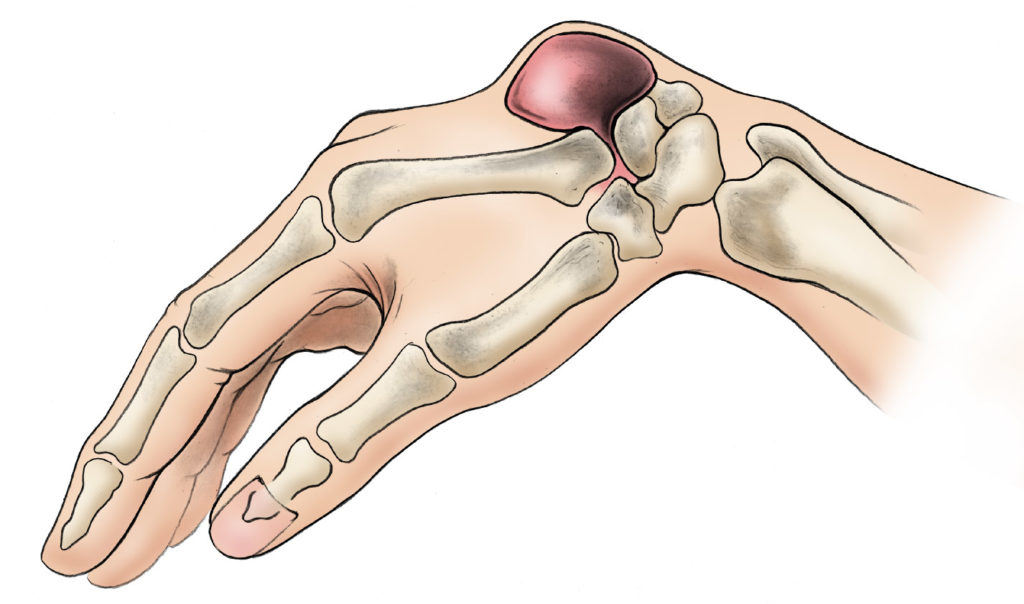
Ganglion cysts are the most common lumps seen around the wrist joint. They commonly develop along the tendons or joints. Most of the ganglions are painless, but sometimes cause pain and disability says Dr Deepthi Nandan Reddy Adla ,Senior Consultant Orthopedic Surgeon Continental Hospitals
How to identify?
Ganglion cysts are typically round or oval and are filled with a jellylike fluid. Small ganglion cysts can be pea-sized, while larger ones can be around an inch (2.5 centimeters) in diameter. Ganglion cysts can be painful if they press on a nearby nerve. Their location can sometimes interfere with joint movement.
The lump most commonly occurs on the back of the hand at the wrist joint but they can also develop on the palm side of the wrist. When found on the back of the wrist, they become more prominent when the wrist is flexed forward. Other sites, although less common, include fingers, feet and other joints.
What causes Ganglion Cyst?
The exact reason behind the development of ganglion cyst or a lump is not yet established. One reason may be increased pressure in the joint, forcing the joint fluid to push through a flaw in the joint capsule(covering) or tendon sheath that allows part of the joint covering tobbulge out with fluid inside it. This flaw acts as a one-way valve mechanism and fluid keeps entering the newly formed cyst and the water content in the fluid reduces leaving a jelly like substance behind in the cyst. some times an injury can cause a defect in the ligament which can be the point of least resistance for the joint fluid to escape and form a cyst. Hence sometimes a ganglion cyst may be associated with ligament injury which may need addressing.
Ganglion Cyst Symptoms
Most ganglion cyst are painful when they appear, but the pain improves naturally and a painless lump remains. The ganglion cyst usually changes in size.
If pain is present, it is usually chronic and made worse by joint motion.
When the cyst is connected to a tendon, you may feel a sense of weakness in the affected finger.
Who is at risk of getting a ganglion cyst?
Ganglion cysts can occur in anyone, but are more commonly seen in women between the age of 20 to 40.
Patients who have Osteoarthritis are more prone to develop Ganglion cysts. People who have wear-and-tear arthritis in the finger joints closest to their fingernails are at higher risk of developing ganglion cysts near those joints, these are called mucous cysts
Joints or tendons that have been injured in the past are more likely to develop ganglion cysts.
What is the treatment of a wrist ganglion?
Most cysts resolve or reduce in size, but some of them can be painful and increase in size. Most ganglion cysts donot require any intervention, but need assessment to confirm the diagnosis.
The cysts which are painful require surgery. Traditionally the cysts are removed by open surgery. Injections and cyst aspirations have been tried but recurrence is high. The new form of treatment is arthroscopy or keyhole surgery
Wrist arthroscopy’, best option to remove Ganglion Cysts-
Ganglion cysts can be treated with wrist arthroscopy by making small cuts on the wrist. A small diameter specially made arthroscope is introduced into the wrist through the small cuts to visualize the iside of the wrist joint, the ganglion is visualized and opened from inside the joint. As the ganglion araises from the joint, it is logical to approach it from thejoint and tackle the root of the problem. Arthroscopy helps in detecting other problems in the wrist joint which may have been missed on routine clinical examination and investigations like X rays and scans. Ganglion cyst removal is usually a daycare procedure and may be performed under regional or general anaesthesia. Studies have shown less recurrence and stiffness when compared to open surgeries, but surgeon experience is the key for reducing complications.
Recovery post ‘Wrist arthroscopy’
After your surgery, the area of the cut will be covered in a bulky bandage that compresses and supports the wrist. Fingers should move freely, and finger movement is often encouraged to limit swelling and stiffness. Your surgeon will provide instructions on caring for your wound, therapy, safe activities and any work or exercise restrictions. Elevating the wrist is important to prevent swelling and pain after surgery.
Are there any complications of the procedure?
Every surgical procedure has complication which can occur. Wrist arthroscopy is to be done by orthopaedic surgeons, who have been trained in the procedure in dedicated hand and wrist units. It requires a high degree of skill and training and lack of this training can increase risk of damaging the joint and the various nerves, tendons and the blood vessels around the wrist as the wrist is surrounded by some very vitals structures which help in hand function. Risk of infection is also described.
